What was once known as the Baby Boom is now becoming a Senior Boom. By 2050, the number of older adults in the United States (ages 65 and up) is projected to increase by 47% compared to 2022, driven by a rapidly aging population.
It’s a pattern that’s emerging far beyond the borders of the US, and is aimed to challenge home care agencies around the world. With 90% of older adults expressing a preference for aging in place, home care organizations need to prepare themselves for increasing demand against a backdrop of rising costs and a strained labor market.
The aging global population calls for a diversified and expanded workforce. And if agencies want a fighting chance at meeting this unprecedented need, they will also need to get creative with their service delivery models.
Individuals born at the tail end of the baby boom – i.e. the mid 1960s – are now reaching their golden age. That means more people than ever will soon be looking into all types of home care, from assistance with daily activities (grooming, housekeeping, etc.) to more intensive medical intervention.
In the US, someone who is 65 today has a 70% chance of requiring some type of long-term care moving forward, whether medical or non-medical. This wave of demand is already building, and given how long it can take to implement change, agencies would be well-suited to start thinking about their growth as soon as possible.
Summary
A rapidly aging population is driving unprecedented demand for home- and community-based care, even as affordability challenges, rising operating costs, and caregiver shortages strain agencies. Technology—especially modern home care software—can enhance efficiency, data-driven planning, and communication, while payer diversification and workforce strategies stabilize revenue and staffing. Policy shifts like Medicaid’s 80/20 provision will shape reimbursement and wages, making regulatory awareness critical. Agencies that invest and adapt now will be best positioned to meet surging needs.
Financial Implications of an Aging Population
While the demand for long-term care is undeniably on the rise, it’s unclear whether many people who need this type of care will be able to afford it. At the same time, the cost of expanding services and reinforcing team sizes is sure to place a similar burden on agencies.
In the US, an assisted living facility costs more per month than many people’s salaries. The median monthly rent is $5,511 – or just over $66,000 per year. While the exact amounts vary by state, this broadly represents a cost that is simply not feasible for countless Americans. In response to these sky-high prices, many of them are turning to in-home care.
According to the National Council on Aging, 80% of older Americans are not in a financial position to pay for long-term caregiving services – specifically, they were found to be “unable to sustain a financial shock such as [LTC] or the loss of income due to divorce or widowhood.”
On the provider side of things, as agencies pivot their strategies to prepare for the oncoming wave, they will take on their fair share of expenses, from conducting market research to hiring additional staff at competitive wages.
Technological Innovations in Home Care
All of these factors point to a pivotal moment on the horizon for agencies – but they won’t be alone in their transformation. We also happen to be in the golden age of technology for home healthcare, with countless innovations hitting the market to improve patient outcomes, enhance efficiency, and offer more personalized care.
In the world of home care, efficiency boils down to one simple thing: how many patients can you see in a day without compromising on quality of care? While manual scheduling leaves plenty of room for human error with very limited flexibility, home care software uses automation to optimize routes, match caregivers to patient needs, and fill open shifts.
Implementing digital transformation at scale is no simple feat. Agencies need to account for challenges like varying degrees of tech-savviness among caregivers, data security concerns, and compatibility issues with existing tech infrastructure. The right home care software will provide the necessary support to nail your onboarding and training, plus robust data security and HIPAA compliance protocols.
Strategies for Home Care Agencies
In addition to leveraging home care software, there are plenty of strategies home care agencies can employ to address the challenges and opportunities presented by the aging population. Slowly but surely, implementing these changes will reinforce the overall health of your business and balance sheet.
Cost Management & Service Optimization
Implementing home care software opens up multiple avenues for managing expenses and optimizing service delivery. Particularly through optimized resource allocation, for example, the ability to intuitively schedule caregivers based on the distance between visits or filling open shifts with pre-determined criteria. Being able to gaining insight into company data at a glance aids in analyzing efficiency, with business intelligence tools removing the guesswork. Additionally, the ability to quickly schedule new shifts or make shift changes through two-way chat or mobile apps ensures that providers stay connected to the office, even while on the go, meaning enhancing responsiveness and reducing operational costs and manual efforts.
Diversification & Specialization
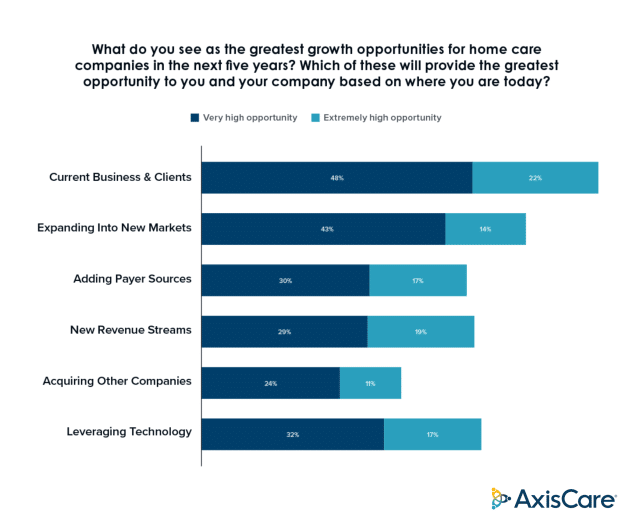
When it comes to revenue sources, putting your eggs in one basket is a huge liability. What if business from that payer source dries up, either temporarily or long-term? The benefits of diversification are twofold: not only does it reduce financial risk, but opening your services up to different groups – whether it’s Medicaid, Medicare, private pay – broadens your pool of potential customers. In fact, according to a third-party study commissioned by AxisCare, 47% of survey participants found a “High” or “Extremely High” opportunity for growth in the addition of payer sources to their service offerings.
Workforce Development & Retention
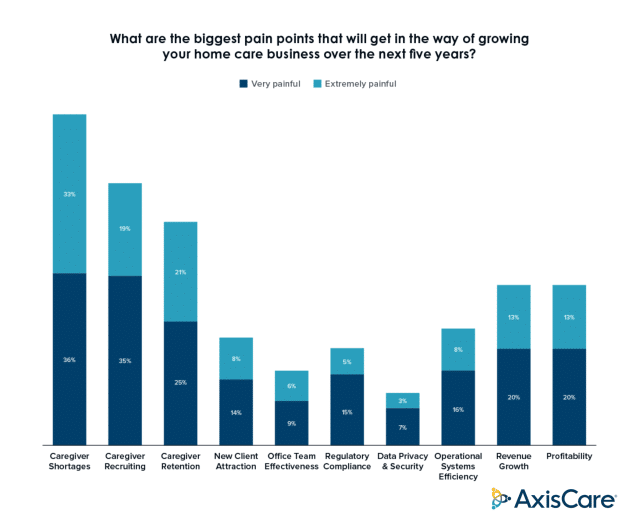
In the aforementioned study, home care organizations are very preoccupied with staffing issues. They identified recruiting systems as a key pillar in ensuring their success and longevity, while acknowledging that attracting and retaining talent is a significant perennial issue: nearly 70% of agencies surveyed identified caregiver shortages as “Very Painful” or “Extremely Painful” as a barrier to growth.
Strengthening your workforce is a goal that can be attacked from many angles. Delivering additional value through benefits and incentives for caregiver retention, leveraging AI for intelligent recruiting, and making caregivers’ jobs easier through technology are just a few of the many strategies agencies can adopt.
The Role of Government Policies
Government policies have shaped the home care landscape in many ways, identifying both successful initiatives and areas in need of improvement. Most recently, in April 2024, the Ensuring Access to Medicaid Services rule introduced significant adjustments to how Medicaid can reimburse home and community-based services. Most importantly, the 80/20 provision states that 80% of those reimbursements must directly support caregiver wages.
Understanding where the law stands today, while turning an eye to future policy development, will prevent agencies from being blindsided or caught without a plan.
The Policy Puzzle
Government policies reach far and wide, putting forth requirements and standards that ensure care quality and patient safety. They also determine funding mechanisms and reimbursement rates for public programs like Medicare and Medicaid, as well as tax incentives or credits to make home care more affordable for patients and their families.
Policies also contribute to creating and expanding home care programs that cater to specific (and often disadvantaged) populations, such as elderly or disabled. individuals. On the agency side, the government puts forth frameworks for caregiver training, certification, and wages, while providing grants and funding to spur innovation and technology integration within the industry.
Implementing Supportive Policies
While new laws are being passed all the time, that doesn’t mean it’s easy to get legislation across the finish line. These efforts require extensive lobbying and collaboration with agencies, patient advocacy groups, and other stakeholders, and securing funding for new or expanded programs is a major challenge. Those funds are often pulled from the same pool of money as other healthcare initiatives, and these efforts can quickly be curbed by budget constraints or economic downturns.
It’s also no simple task to integrate home care services into public and private insurance plans; the process typically requires negotiations with the insurers themselves. On the whole, successfully implementing new policies usually requires coordination between multiple stakeholders and government agencies, which can be difficult to manage.
The Time to Act is Now
Businesses should constantly be innovating and adapting, but home care agencies should be especially tapped in given the incoming influx of aging Americans.
If you don’t already have home care software in place, or if you’re not satisfied with the one you’re currently using, now is the time to get on the right track. Schedule a live demo with AxisCare, the industry’s #1-rated home care software.
FAQs
Demographics and preferences are converging. Adults 65+ in the U.S. are projected to grow by 47% by 2050 compared to 2022, most older adults (about 90%) prefer to age in place, and someone turning 65 today has a 70% chance of needing some form of long-term care. High facility costs further steer families toward in-home options, together creating unprecedented demand.
Affordability is a major barrier for families—assisted living costs a median $5,511 per month, and 80% of older Americans are not positioned to pay for long-term care or withstand a major financial shock. Agencies, meanwhile, face rising operating costs to scale services and staffing. This dual squeeze makes cost-efficiency, payer diversification, and prudent growth planning essential.
Software boosts efficiency and communication without compromising care quality. Automation can optimize schedules and routes, match caregivers to client needs, and fill open shifts. Business intelligence tools surface performance insights, while two-way chat and mobile apps keep field staff connected and responsive. Robust onboarding support plus HIPAA-grade security helps agencies adopt technology confidently and compliantly.
Successful digital transformation requires addressing caregiver tech-savviness, protecting data, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Choosing the right platform matters—look for strong training and onboarding, built-in data security and HIPAA compliance, and features that integrate smoothly into current workflows to minimize disruption and maximize adoption.
Policy shifts directly influence reimbursement, staffing, and wages. Under the Ensuring Access to Medicaid Services rule, 80% of certain Medicaid HCBS reimbursements must go to caregiver wages, reshaping margins and payroll strategies. More broadly, regulations set quality standards, training frameworks, and funding mechanisms—but implementation can be complex, requiring coordination with payers and stakeholders. Staying proactive on policy is critical to avoid operational surprises and to plan sustainable growth.